Home » Discovering Wi-Fi 6E Technology
Wi-Fi 6E represents the forefront of wireless technology, extending the capabilities of Wi-Fi 6 into the 6 GHz frequency band. This advancement not only promises faster speeds and greater capacity but also less interference, catering to the growing demand for high-bandwidth applications in our digital era.
Its relevance is particularly significant for professionals pursuing CCIE Wireless training certification, as it underscores the evolving landscape of wireless networks. Understanding Wi-Fi 6E is crucial for these experts, ensuring they stay abreast of cutting-edge technologies that shape modern wireless infrastructures and solutions.
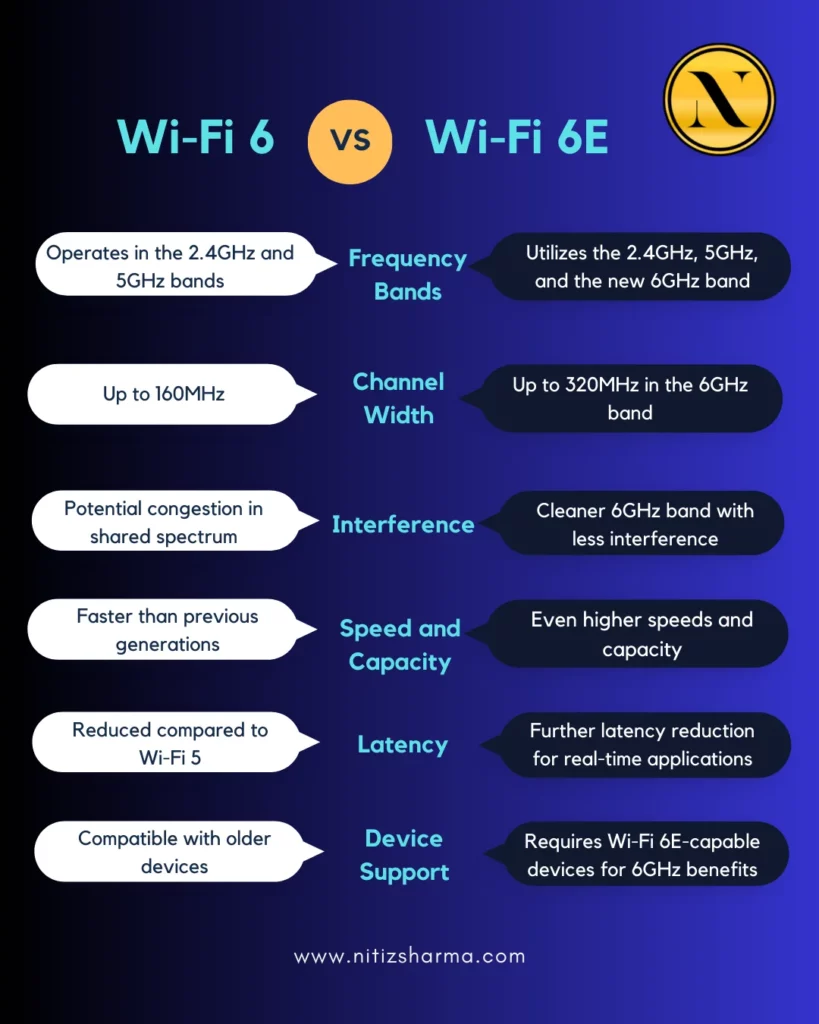
Wi-Fi 6E is a significant leap in wireless technology, extending Wi-Fi 6’s capabilities by utilizing the newly opened 6 GHz frequency band.
This addition effectively triples the amount of spectrum available, offering 14 additional 80 MHz channels and 7 additional 160 MHz channels, which are essential for high-bandwidth applications. 6E supports higher data rates, up to 9.6
Gbps, and uses both the existing 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands alongside the new 6 GHz spectrum. This enhancement not only improves throughput but also reduces congestion and interference, providing a more reliable and efficient wireless experience.
As an evolutionary step, Wi-Fi 6E builds upon the strengths of Wi-Fi 6. It retains key features like OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access), MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output), and 1024-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation).
These technologies enable more efficient data encoding, allowing multiple devices to communicate simultaneously, thus improving network capacity and efficiency. Wi-Fi 6E is poised to revolutionize applications requiring high data throughput and low latency, such as virtual reality, ultra-high-definition streaming, and cloud computing.
For CCIE Wireless professionals, this table underscores the importance of Wi-Fi 6E’s improvements over Wi-Fi 6, particularly in terms of spectrum availability, bandwidth, and reduced congestion and interference.
This knowledge is key for designing and managing advanced wireless networks in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Technical Operation:
Efficiency and Performance:

Wi-Fi 6E offers several significant benefits, crucial for both everyday users and professionals in the field of wireless networking, particularly those pursuing CCIE Wireless certification.
Hardware Compatibility:
It’s advanced capabilities necessitate specific infrastructure requirements, particularly in hardware compatibility and network infrastructure. To fully utilize Wi-Fi 6E, users must upgrade to routers and devices that support the 6 GHz band, as older devices are limited to 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies. This means investing in Wi-Fi 6E-compatible routers, smartphones, laptops, and other IoT devices to experience the enhanced speed and capacity.
Network Infrastructure:
In terms of network infrastructure, existing Wi-Fi networks may require an overhaul to support the new standard. This includes updating network switches and access points to handle increased data rates and ensure seamless operation across the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands.
Practical Use:
Industry-Specific Needs:
Wi-Fi 6E, advancing into the 6 GHz band, significantly boosts wireless technology with increased speeds, reduced congestion, and higher device capacity, benefiting high-bandwidth applications and dense device environments.
Its evolution, likely integrating with AI and machine learning, promises broader industry adoption and enhanced user experiences. For CCIE Wireless professionals, understanding and leveraging Wi-Fi 6E is vital for designing and managing advanced wireless networks.
This technology not only enhances current capabilities but also sets a precedent for future wireless standards, focusing on efficiency and speed, essential in the evolving landscape of wireless communication.
