Network security authentication is a critical cornerstone in safeguarding digital information. It acts as the first line of defense in confirming users’ identities before granting access to sensitive data and systems. In today’s digital era, where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, robust network security authentication methods are essential.
They not only protect against unauthorized access but also build a foundation of trust in digital interactions, ensuring that personal and corporate data remain secure. This significance is amplified as businesses and individuals rely heavily on online platforms for their daily operations and communications.
Network security authentication is a fundamental process used to verify the identity of users or entities trying to gain access to secure networks and systems. It serves as a vital security checkpoint that determines whether someone or something is, in fact, who or what it claims to be.
This process is pivotal in safeguarding sensitive information and resources from unauthorized access, ensuring that only legitimate users can interact with the protected data or systems.
The purpose of network security authentication extends beyond mere identity verification. It plays a key role in mitigating cyber threats and boosting an organization’s security stance.
Robust authentication reduces data breaches, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access risks, crucial in an era of sophisticated cyber threats. It serves as a gatekeeper, thwarting attackers from exploiting weak or stolen credentials to access sensitive systems.
Network Security authentication is essential in protecting sensitive data. In sectors like finance, healthcare, and government, where the handling of confidential information is routine, effective authentication ensures that only authorized personnel can access and interact with this data.
This not only helps in maintaining data integrity and confidentiality but also aids in complying with various regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, etc., which mandate stringent data protection measures.
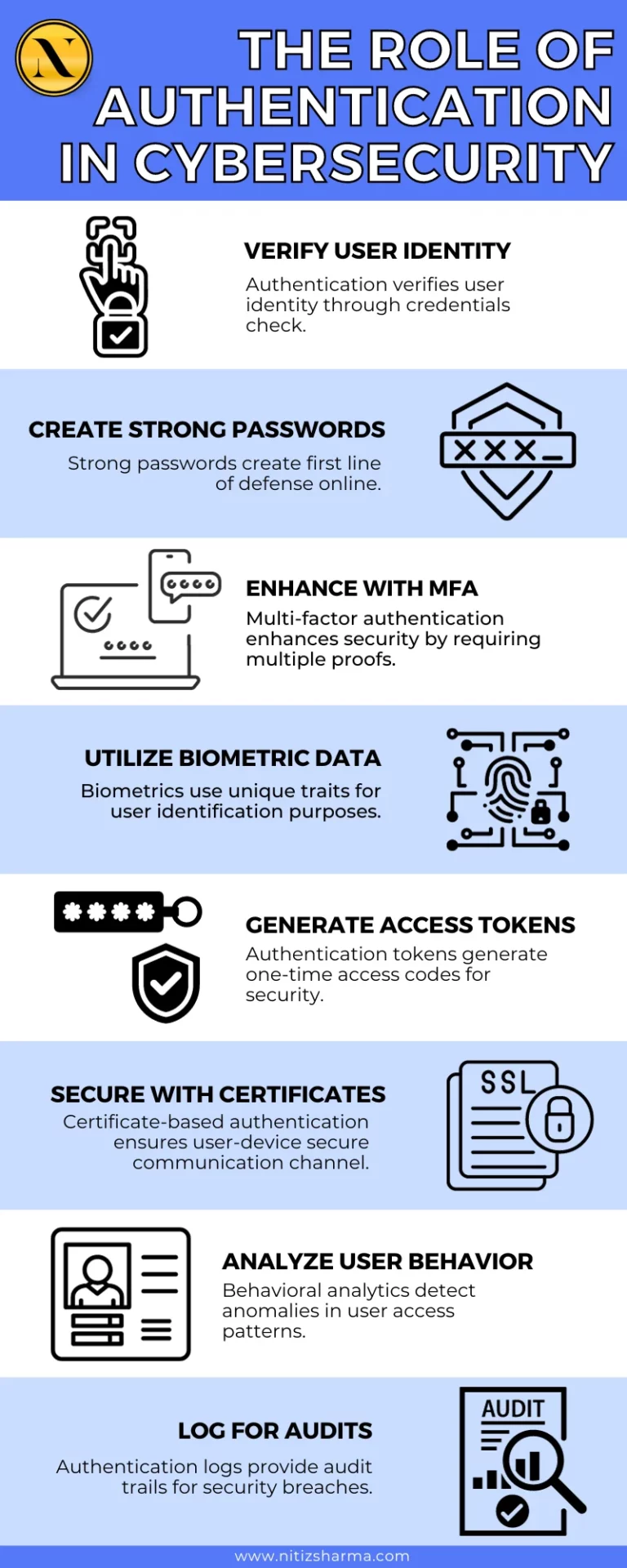
Network security authentication methods are diverse, each offering unique benefits and levels of security. The most common methods include passwords, biometrics, token-based systems, and certificate-based authentication.
Passwords are the simplest and most widely used form of authentication. They rely on the user providing a secret word or phrase. While password-based authentication is user-friendly, its security depends heavily on password strength and confidentiality. It’s vulnerable to attacks like phishing and brute force.
Biometrics, identifying individuals through unique physical characteristics like fingerprints or facial recognition, offers sophisticated security. Highly secure and nearly impossible to replicate, this method requires specialized hardware. While effective in verifying identities, it also presents potential privacy concerns due to the sensitive nature of the data involved.
Token-based authentication employs physical or digital tokens, like security keys or apps generating one-time codes, for system access. Users need the token and the code for entry. This method enhances security over traditional passwords by generating unique codes at each login, effectively reducing unauthorized access risks.
Certificate-based authentication uses digital certificates to verify public key ownership. These certificates contain key details, owner identity, and a verifier’s digital signature, commonly used in securing email communications and website authentication.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring two different authentication factors. Typically, this combines something the user knows (like a password) with something the user has (like a token or a biometric trait). 2FA significantly enhances security by ensuring that a compromised password alone is not enough for an intruder to breach a user’s account.
These authentication methods form the backbone of network security, providing various levels of protection and usability. Choosing the right method depends on the specific needs and security requirements of the organization or user.
Network security authentication protocols are essential frameworks that dictate how authentication should be carried out securely. Among the most common protocols are OAuth and Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML).
OAuth is an open standard for access delegation, widely used for token-based authentication and authorization online. It lets users grant controlled access to their information on one site to another site or application, without sharing passwords.
By issuing tokens for specific resources over a set period, OAuth enhances security, reducing the exposure of user credentials and limiting access, thus enabling a more secure, user-centric approach to digital security and data privacy.
SAML, on the other hand, is an XML-based framework for communicating user authentication, entitlement, and attribute information. It is widely used for enabling single sign-on (SSO) for enterprise-level applications, allowing users to log in once and gain access to multiple systems without re-authenticating.
SAML facilitates the secure transmission of authentication tokens and user information between the identity provider (the entity that verifies the user’s identity) and the service provider (the entity that needs the user identity verified).
Authentication protocols are crucial for verifying user identities and securing vulnerabilities. They prevent frequent transmission of sensitive credentials, reducing interception risks. These protocols standardize authentication, facilitating robust security practices and secure system integration.
When combined with measures like encryption and two-factor authentication, they form a multi-layered defense against cyber threats. This integrated approach is vital in today’s interconnected digital world for protecting sensitive data and systems from various cyber risks.
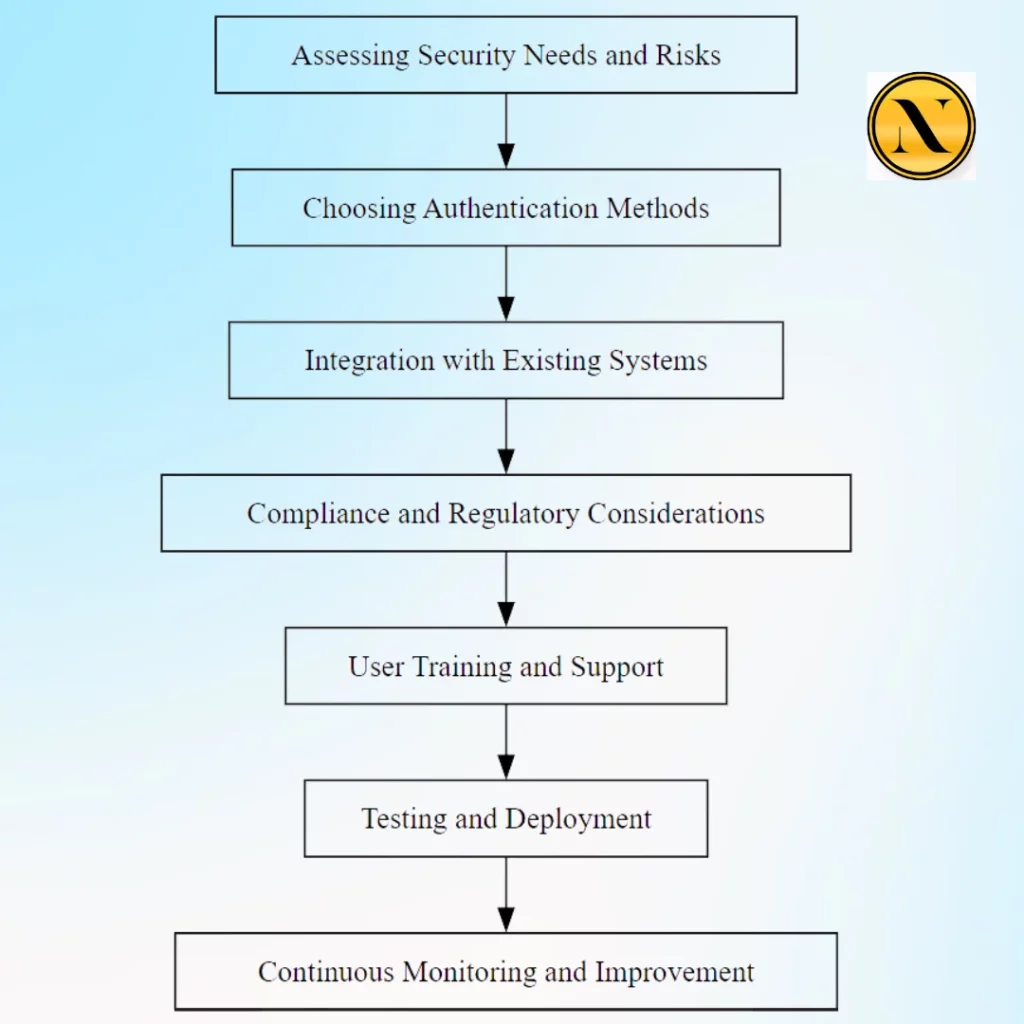
A relevant case study is the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) at a financial services company. Facing increasing cyber threats, the company decided to implement MFA to protect client data and financial transactions.
The implementation involved user training sessions, a phased roll-out, and continuous support to address user concerns. The result was a significant reduction in phishing attacks and unauthorized access attempts, demonstrating the effectiveness of MFA in enhancing organizational security.
Network security authentication faces several challenges in the current digital landscape.
To address these challenges:
Finally, continuous monitoring of authentication systems and user behaviors can help in early detection of suspicious activities. This, combined with a rapid incident response plan, can significantly mitigate the impact of any security breaches.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can strengthen their authentication processes and better protect against the evolving threats in network security authentication.
Network security authentication is pivotal for businesses in maintaining their integrity, trustworthiness, and operational continuity. In an era where digital transactions and data exchanges are commonplace, the importance of robust authentication mechanisms cannot be overstated.
Effective authentication serves as a gatekeeper, ensuring that access to sensitive business data and systems is granted only to authorized individuals. This not only helps in protecting against data breaches and cyber-attacks but also plays a significant role in preserving the confidentiality and integrity of critical business information.
Impact on Trust:
Impact on Compliance:
Impact on Business Continuity:
In conclusion, the field of network security authentication is continually evolving, adapting to new challenges and technological advancements. Its critical role in protecting digital assets and maintaining the integrity of online systems cannot be overstated.
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the importance of robust authentication mechanisms grows. The future of authentication lies in innovative technologies like AI, machine learning, and advanced biometrics, promising enhanced security and user experience.
Organizations must stay abreast of these developments, integrating adaptive and user-centric authentication strategies to safeguard their digital landscapes effectively. This continuous evolution is essential in upholding the security and trust essential in today’s digital world.
